Adult Cystic Fibrosis Clinic - provider info
Information here is intended for health care providers who have patients living with cystic fibrosis (CF).

Provider info
Information here is intended for health care providers who have patients living with cystic fibrosis (CF).
We encourage health care providers to contact the Adult Cystic Fibrosis Clinic to liaise with our clinic respirologists, who are specialists in cystic fibrosis. All people with CF in BC should be registered with a cystic fibrosis clinic for regular, specialized care.
Treatment for Distal Intestinal Obstruction Syndrome (DIOS)
This is a severe form of constipation that can occur in people with CF. Patients who have had previous episodes of DIOS have developed a treatment strategy that has worked for them.
Emphasis is non-surgical management since most episodes are self-limited and resolve with conservative medical management. Please contact the clinic at 604-806-8522 to seek guidance about treatment.
Medication coverage
People with cystic fibrosis receive coverage for digestive enzymes and other products under Pharmacare’s Plan D Cystic Fibrosis Formulary.
People with cystic fibrosis may also be eligible for other medication. In some cases this requires Pharmacare Special Authority. Some examples include:
Pulmonary exacerbation management
Many adult patients with cystic fibrosis are chronically infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and/or Staphylococcus aureus. A minority of patients grow Burkholderia cepacia, a complex that includes a number of different species/gemnovars. Other organisms that may be seen include: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Achromobacter xylosoxidans, non-tuberculous mycobacterium, Exophiala dermatitidis, and Aspergillus spp. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary exacerbations in people with CF can be found on the CF Canada website.
Although many exacerbations can be treated with oral antibiotics, some patients experiencing a CF pulmonary exacerbations may require IV antibiotics in the hospital or community setting. Treatment of pulmonary infection due to either P. aeruginosa or B. cepacia requires the use of two antibiotics. Antibiotics are primarily selected based on previous response to therapy, sputum cultures, and known antibiotic intolerances or allergies. Doses of most antibiotics are higher in people with CF, because they often clear antibiotics faster than people in the general population. Antibiotic dosing guidelines for people with CF can be found on the CF Canada website.
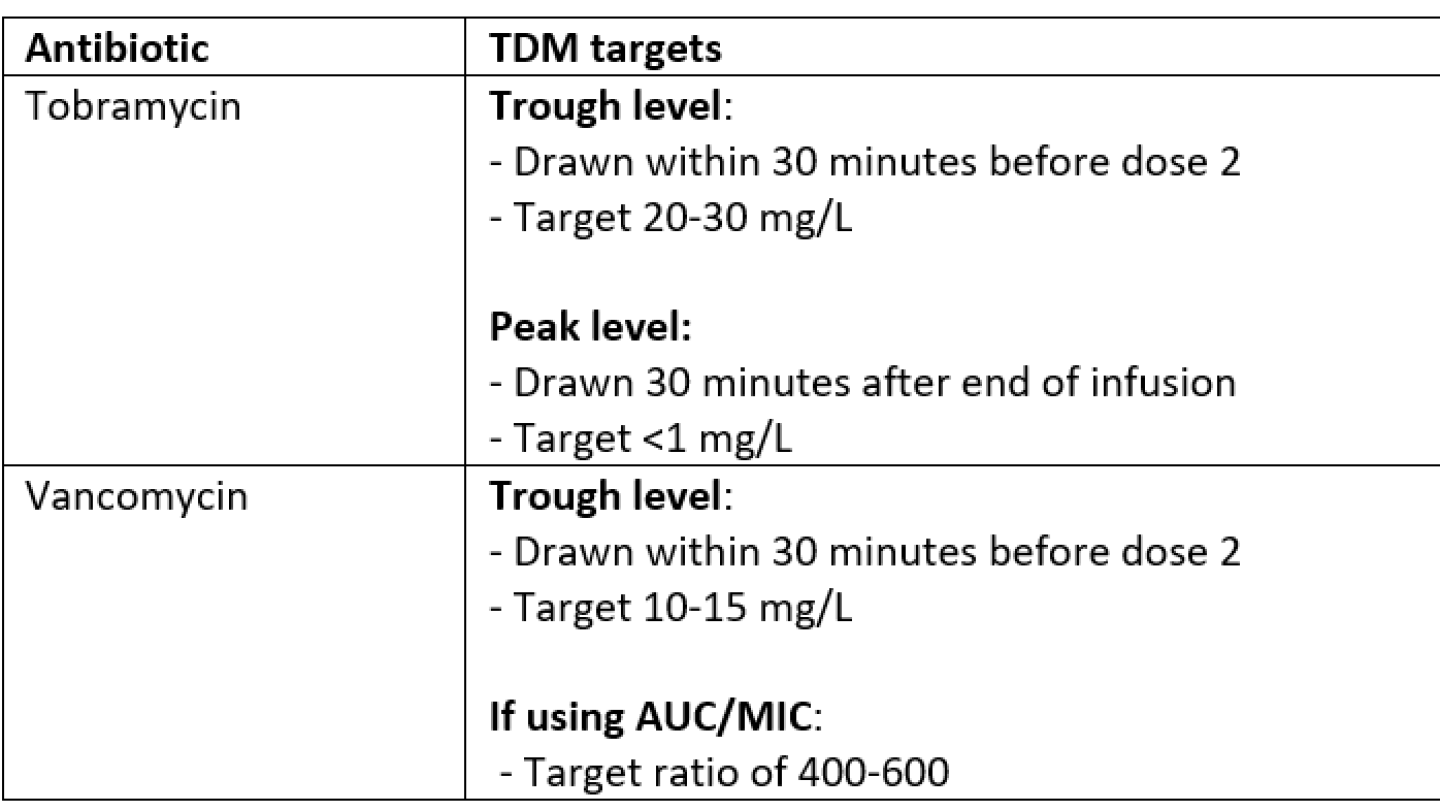
If IV aminoglycosides or vancomycin are prescribed in the hospital or community setting to treat a pulmonary exacerbation, therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is necessary to optimize the effectiveness and safety. The target levels recommended at our site are:
Last reviewed: August 27, 2024
